What does a GIS Analyst Do?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are becoming increasingly important in today’s data-driven world. As businesses collect and analyze large amounts of data, GIS Analysts play a critical role in turning that data into useful insights. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the responsibilities of a GIS Analyst, the skills required, and potential job opportunities in the field.
GIS Analyst Responsibilities
GIS Analysts are responsible for integrating various data sources using GIS software to provide insights into business decisions. This involves working with workflows to ensure that data moves throughout the company seamlessly. Analysts may also be responsible for integrating geo-databases and curating data repositories for the business.
Another essential responsibility of a GIS Analyst is to have a good understanding of the industry they work in. They need to know the problems businesses face and supplement the information collected to make informed decisions. Analysts also need to think spatially and understand how data can be stacked on top of each other to analyze spatial relationships.
Skills Required for a GIS Analyst
To become a successful GIS Analyst, several skills are necessary. Analysts need a good understanding of statistics, math, and databases. They also need to have strong problem-solving skills, as they will be responsible for identifying and solving issues that may arise. Excellent communication skills and presentation skills are also crucial, especially if you want to advance into a management role.
GIS Analysts are often required to have at least a bachelor’s degree in a related field, such as geography, GIS, or computer science. While some companies may not require a degree, having one will give you an advantage in the job market.
GIS Analysts require a mix of technical and soft skills. Some of the key technical skills required to be a GIS Analyst include:
- Knowledge of GIS software and tools: GIS Analysts must have an excellent understanding of GIS software and tools, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, or alternatives, to analyze and manipulate spatial data.
- Spatial data analysis: GIS Analysts should have strong analytical skills to interpret and analyze spatial data, such as mapping, spatial clustering, and geostatistics.
- Database management: GIS Analysts should have a good understanding of database management systems, such as SQL or Oracle, to manage large spatial databases effectively.
- Programming languages: GIS Analysts should be proficient in programming languages, such as Python, R, or Java, to write custom scripts and automate workflows.
- Data visualization: GIS Analysts should be skilled in creating maps, graphs, and other visualizations to present spatial data effectively.
- Cartography: GIS Analysts should have a good understanding of cartography principles to design and produce high-quality maps for various applications.
- Spatial data modeling: GIS Analysts should be skilled in creating spatial data models to simulate and analyze real-world scenarios, such as land-use change or climate change.
- Geodatabase design: GIS Analysts should have a good understanding of geodatabase design principles to create efficient and scalable spatial databases for organizations.
Cleaning spatial data is an essential technical skill that GIS Analysts require. Spatial data can be messy and contain errors or inconsistencies that can affect the analysis results. Therefore, GIS Analysts need to clean and preprocess spatial data before analysis to ensure the data’s quality and accuracy.
Here are some of the key tasks involved in cleaning spatial data:
- Data verification and validation: GIS Analysts should verify and validate the spatial data to ensure that it’s complete, accurate, and consistent.
- Data cleaning: GIS Analysts should clean the spatial data by removing or correcting any errors, duplicates, or inconsistencies.
- Data normalization: GIS Analysts should normalize the spatial data by converting it into a consistent format and resolution to ensure that the data is suitable for analysis.
- Geocoding and address standardization: GIS Analysts should standardize and geocode the spatial data by converting street addresses or place names into spatial coordinates for analysis.
- Data integration: GIS Analysts should integrate multiple sources of spatial data to create a complete and accurate dataset for analysis.
- Data transformation: GIS Analysts should transform the spatial data into different projections or coordinate systems to ensure that the data aligns with other datasets or maps.
Job Opportunities
The job market for GIS Analysts is expanding, with several job titles to choose from. Besides GIS Analyst, other job titles include Location Intelligence Analyst, Business Intelligence Analyst, and Data Analyst. These jobs may focus on spatial data or business data, depending on the role’s specific requirements.
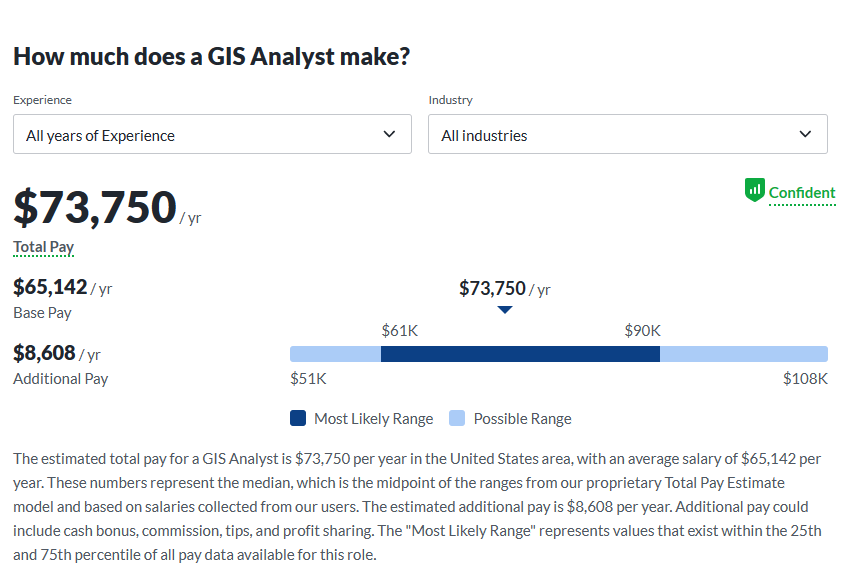
GIS Analyst Salary
Conclusion
GIS Analysts play a crucial role in helping businesses make informed decisions using data insights. The job requires a mix of technical and soft skills, such as problem-solving, communication, and presentation skills. With a degree in a related field, you can find job opportunities in various industries, such as location intelligence, business intelligence, and data analysis. So, if you’re interested in this field, it’s worth considering pursuing a career as a GIS Analyst.